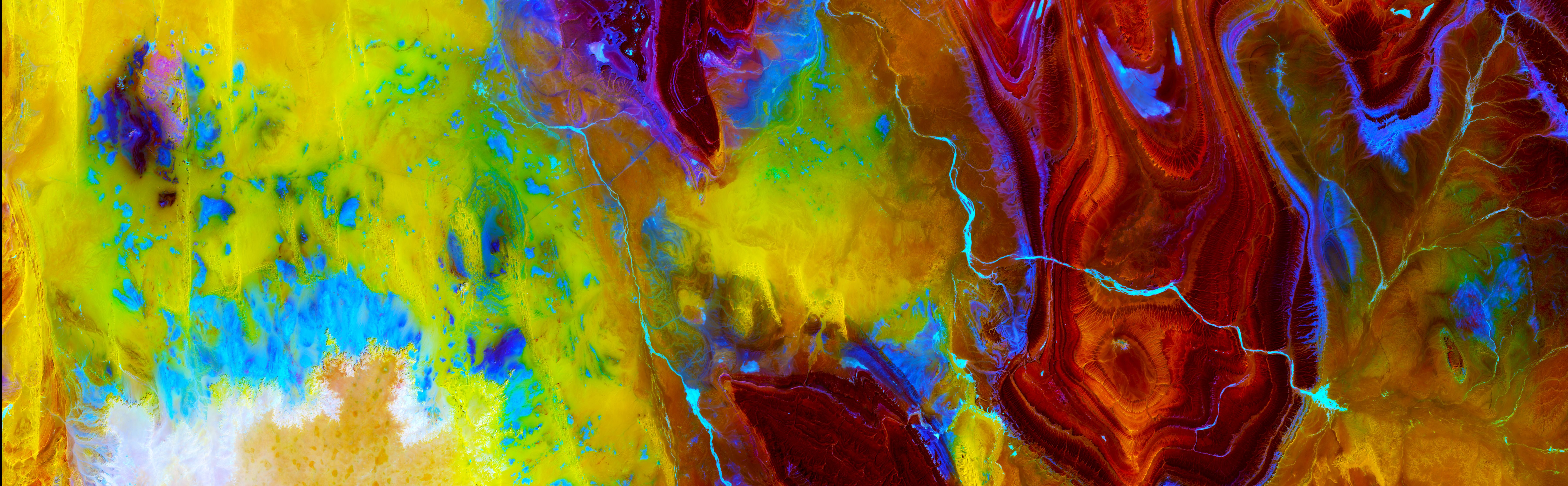
NebraskaView is working with the Nebraska GIS Council to identify high priority issues that can be addressed through remote sensing. We will demonstrate remote sensing applications using products derived from both ongoing Center for Advanced Land Management Information Technologies (CALMIT) research and via new research projects with AmericaView partners.
Urban Tree Canopy Mapping
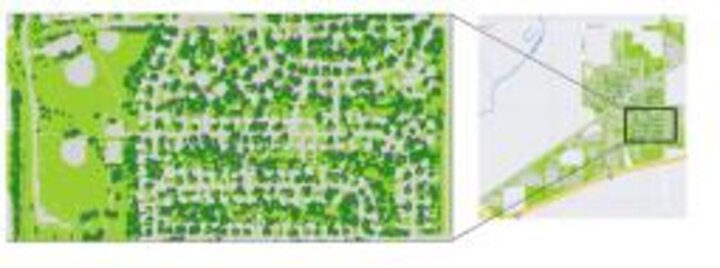
This project continued previous work exploring the use of airborne imagery for urban forestry applications, which included mapping urban tree canopy distribution and classification of specific tree species types. Classification maps for three Nebraska communities were completed.
Urban Forestry Applications
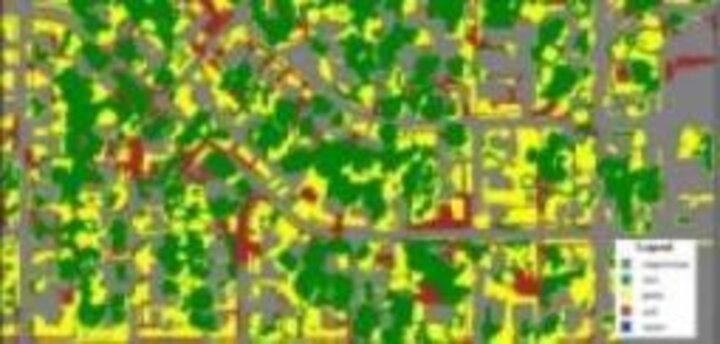
This project explored the use of airborne imagery for urban forestry applications, which included mapping urban tree canopy distribution and classification of specific tree species types.
Emerald Ash Borer Detection
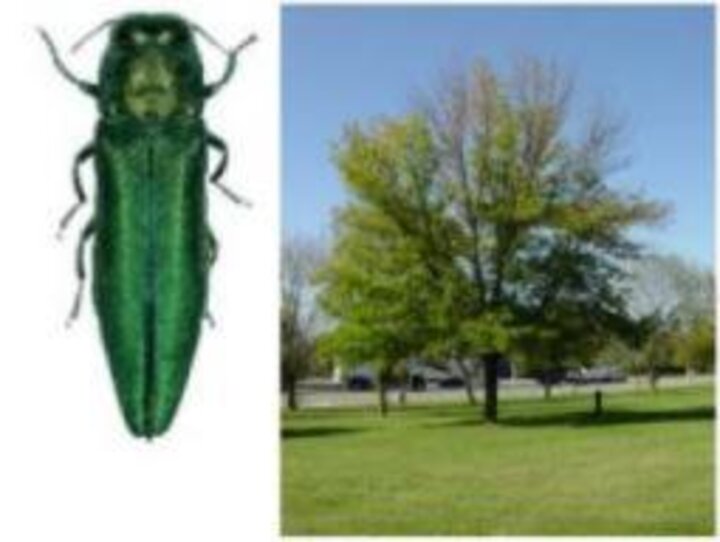

The NebraskaView program partnered with the City of Lincoln Parks and Recreation to assess the utility of airborne remote sensing for detecting and managing emerald ash borer infestations within the city’s urban forests.
Crop Hail Damage Assessment
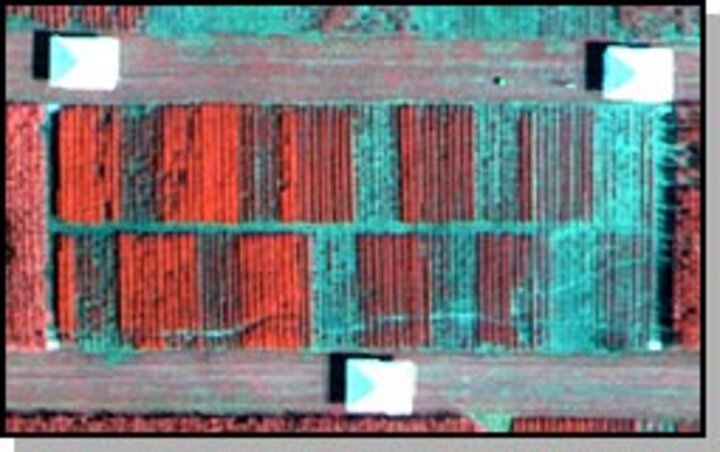
This project demonstrated that commercially available imagery and image processing software tools could be used to detect and locate the relative level of hail damage in cropped areas. Landsat TM imagery was identified as a very useful tool for pre-planning hail-damage assessment operations in a severe storm situation.
Remote Sensing of Carbon Exchange
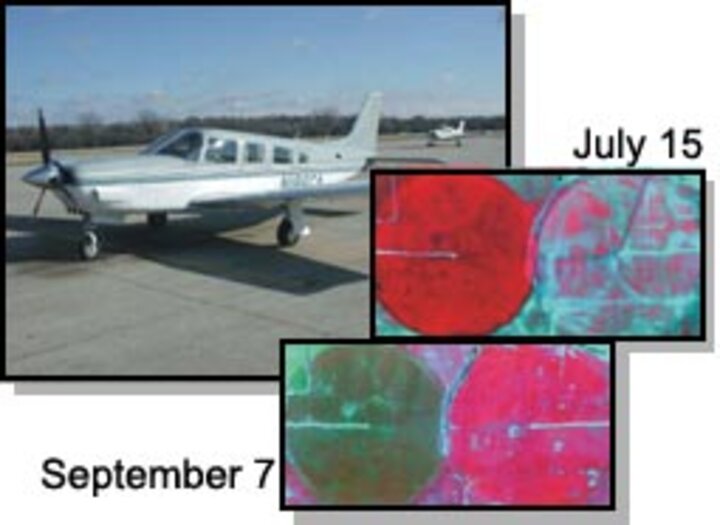

This project evaluated the utility of high-resolution airborne multispectral imagery as an aide to an empirical and simple crop-growth / yield-estimation model. It was shown that timely airborne (or satellite) imagery obtained during the grain fill stage of plant growth is moderately well correlated to grain yield. The usefulness of the imagery is greatest in delineating the relative condition of corn or soybeans in large fields.
Delineation of Land Cover and Land Use for the Central Platte River Basin Cooperative Hydrology Study (1982, 1997 and 2001)
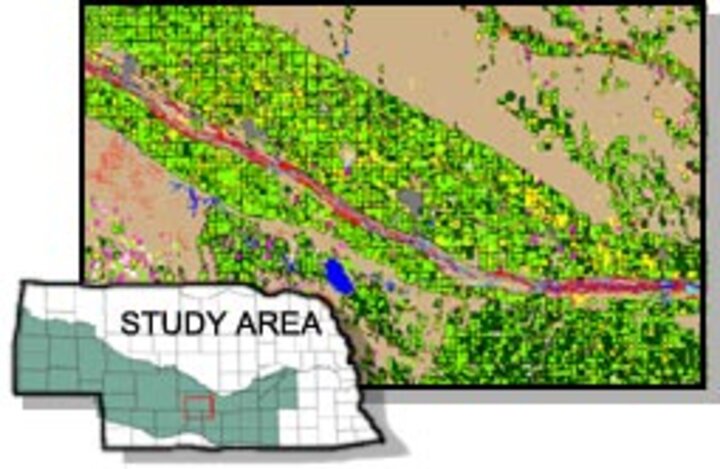
The Cooperative Hydrology Study (COHYST) is a multi-agency project intended to improve understanding of hydrological conditions in the Platte River. COHYST involves assemblage and creation of numerous geospatial data layers to be used in modeling and development of a water resources decision support system (DSS). A critical data layer required for the DSS is a detailed and accurate map of land use. By capitalizing on the seasonal dynamics of the agricultural crops and native plant communities, accurate land cover and land use were mapped using Landsat satellite imagery for three different years: 1982, 1997 and 2001.
Crop Yield Monitoring
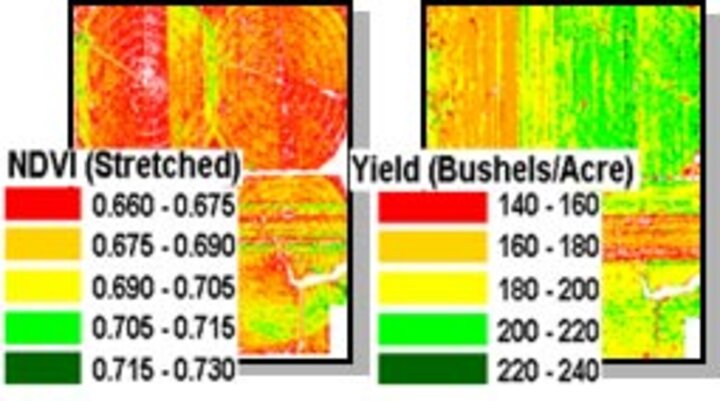
This project evaluated the utility of high-resolution airborne multispectral imagery as an aide to an empirical and simple crop-growth / yield-estimation model. It was shown that timely airborne (or satellite) imagery obtained during the grain fill stage of plant growth is moderately well correlated to grain yield. The usefulness of the imagery is greatest in delineating the relative condition of corn or soybeans in large fields.